Java Module provides operations to integrate with existing Java Classes by enabling your message flows to invoke static or non-static
Java Methods from java classes
Two ways to invoke java methods:
- Java Module from Exchange
- Transform Message component
Use cases
- Integration with custom Java libraries
- Legacy integration
- Performance Optimization
Static Method vs Non Static Method
| Static Method | Non Static Method | |
| Definition | Belongs to class itself not to instances | Belongs to each instance of class |
| Invocation | Accessed using the class name | Accessed using instance of class |
| Memory Allocation | Allocated memory only once | Allocated memory for instance of class |
| Access to member | Can only directly access static members | Can only directly access both static and Non-static members |
| Usage | Used for utility methods or helper functions | Used for operations that require functions |
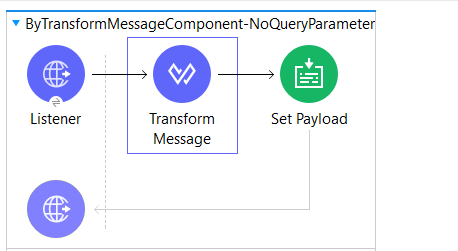
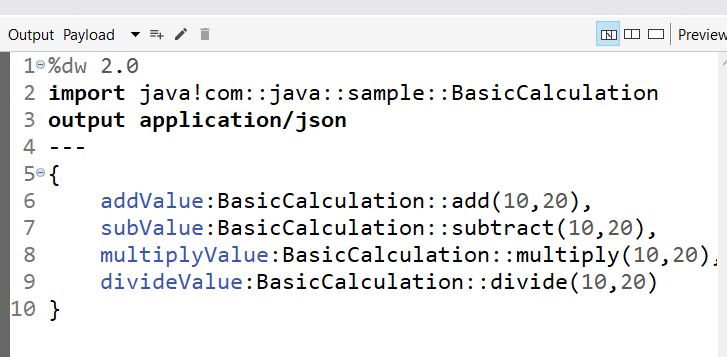
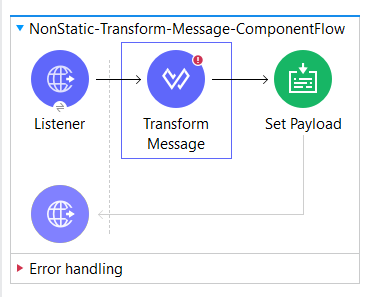
Invoke Static Method by Transform Message:

Instantiate Java class by Transform Message
- Through DataWeave code, you can instantiate a new object of any class
- Can’t call its instance methods through DataWeave
- We can reference its variables.
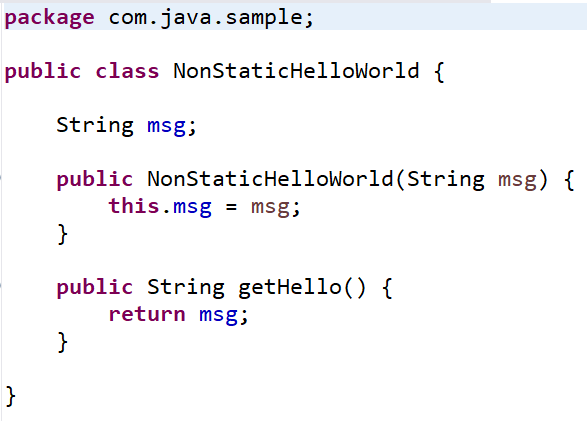
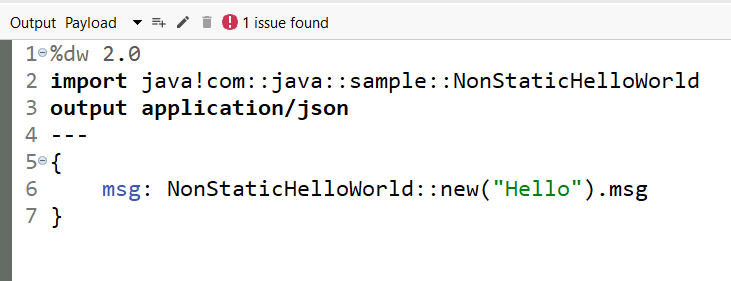
- imports NonStaticHelloWorld
- Creates a new instance of the class, and calls its instance variable msg
- Note that it is not possible for DataWeave to call the object’s call Hello method.
JAVA Module Connector:
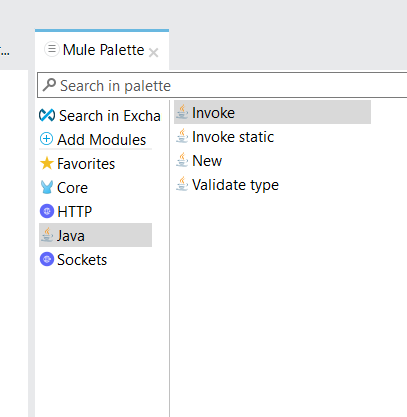
- Invoke Static – This operation of Java Module is used to invoke static methods from a Java Class.
- New – This operation of Java Module is used to create instance of a class. It creates an instance which can be subsequently used to invoke non-static methods of the class.
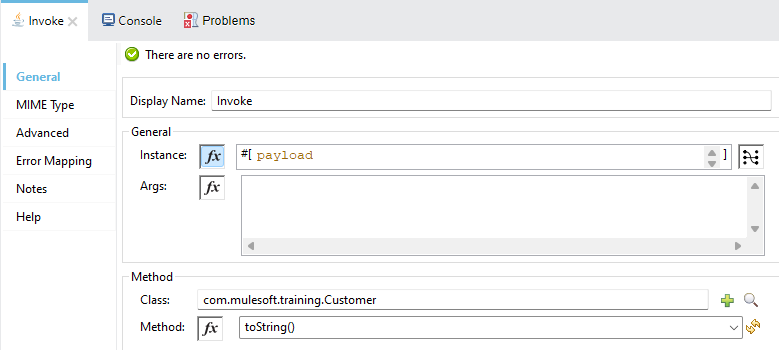
- Invoke – This operation of Java Module is used to invoke methods of a class based on class instance. New operation must be used first to generate the instance and then Invoke can be used.
- Validate Type – This operation can be used to validate type of an instance. It validates that provided instance and class in the configuration match or not. If they don’t match it throws JAVA:WRONG_INSTANCE_CLASS error type
Invoke Static:
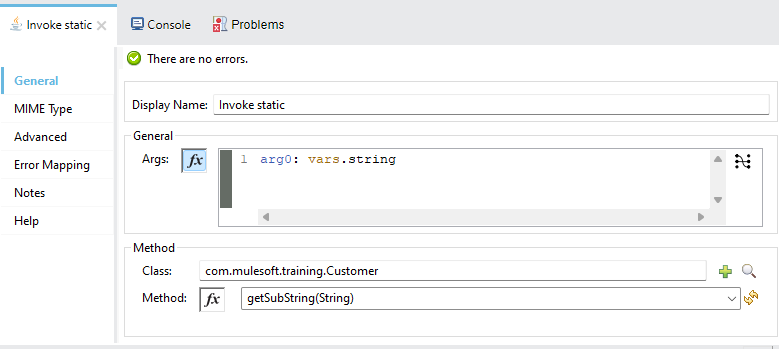
Drag and drop the invoke static connector to call java class and configure the Java Class name as packagename.classname ,methodname and provide the arguments as shown below
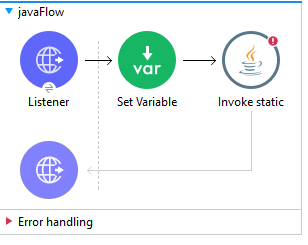
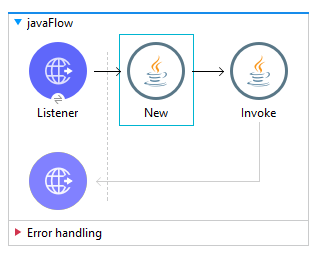
The next step is to instantiate with the New processor and invoke with the Invoke processor the Java class into a Flow.
In the New processor, you have to select the Java class you want to instantiate by selecting its constructor and pass any parameters necessary. Arguments need to be written in JSON format, and the key must match the name of the Java constructor argument.
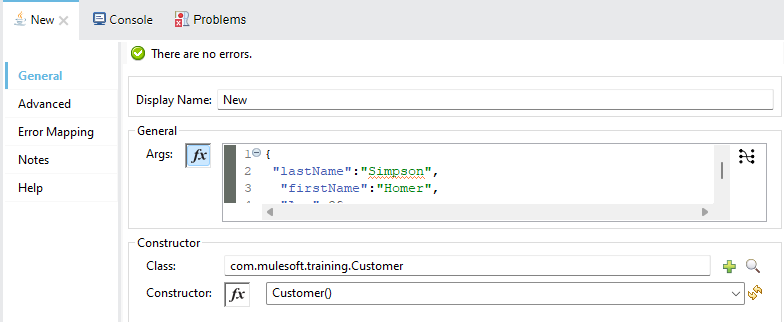
By default, the newly instantiated object is stored in the Mule payload, although you can configure it to be stored in a variable and therefore reference it via vars.variableName
Invoke processor takes by default the input payload as an input and stores the result of the method in the output payload.
Conclusion:
MuleSoft encourages a strategy of maximizing code reuse, which aligns seamlessly with leveraging Java in Mule applications. By integrating existing Java classes into your Mule projects, you capitalize on the investments made in Java development, promoting efficiency and consistency across your application ecosystem. This seamless integration simplifies the adoption of Java components within Mule applications, fostering a cohesive development environment.